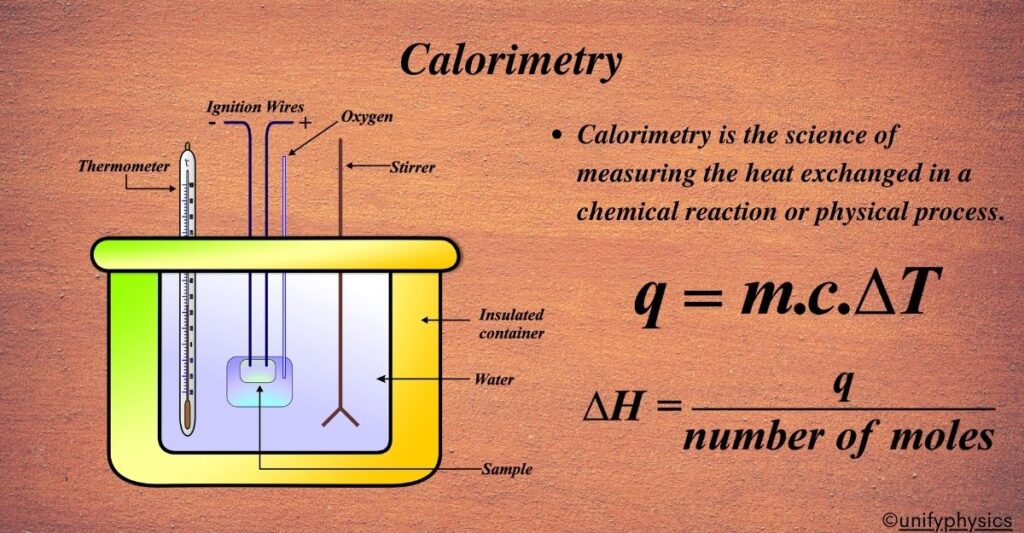
This course provides a structured exploration of calorimetry, the scientific study of heat transfer. It begins with a historical overview of calorimetry's evolution, highlighting its significance in advancing thermodynamics. Learners will examine its applications in chemistry, biology, and food science, developing an understanding of how calorimetric techniques are used to measure energy changes in various processes.
The course also delves into the fundamental differences between heat and temperature, ensuring a clear grasp of these essential concepts. Finally, it integrates the laws of thermodynamics, demonstrating their relevance to calorimetric analysis. Through practical experiments, structured assessments, and competency-based learning approaches, students will gain both theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience in calorimetric applications.
- Teacher: Admin User

