This course provides a structured exploration of calorimetry, the scientific study of heat transfer. It begins with a historical overview of calorimetry's evolution, highlighting its significance in advancing thermodynamics. Learners will examine its applications in chemistry, biology, and food science, developing an understanding of how calorimetric techniques are used to measure energy changes in various processes.
The course also delves into the fundamental differences between heat and temperature, ensuring a clear grasp of these essential concepts. Finally, it integrates the laws of thermodynamics, demonstrating their relevance to calorimetric analysis. Through practical experiments, structured assessments, and competency-based learning approaches, students will gain both theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience in calorimetric applications.
- Teacher: Admin User
Overview
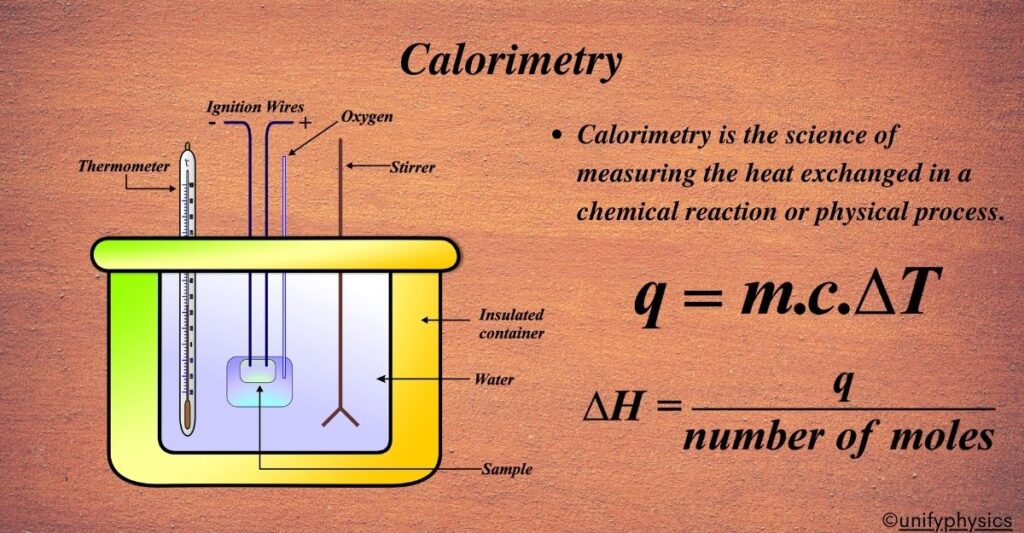
Calorimetry is the scientific measurement of heat transfer in physical and chemical processes. This course will provide students with a comprehensive understanding of calorimetric principles, techniques, and applications in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Course Objectives
- Understand the fundamental principles of calorimetry and its significance in thermodynamics.
- Learn about different types of calorimeters and their appropriate uses.
- Analyze heat transfer in reactions and processes, including phase changes and chemical reactions.
- Conduct calorimetric experiments and interpret data accurately.
Course Topics
-
Introduction to Calorimetry
- Definition and historical context
- Importance in chemistry, biology, and engineering
-
Basic Concepts
- Heat, temperature, and the laws of thermodynamics
- Specific heat capacity and its relevance
-
Types of Calorimeters
- Coffee cup calorimeter
- Bomb calorimeter
- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
-
Quantitative Analysis
- Calculating heat transfer (q) using calorimetric equations
- Enthalpy changes in chemical reactions
-
Applications of Calorimetry
- Calorimetry in biochemical processes (e.g., cellular respiration)
- Industrial applications in material science and energy research
-
Experimental Techniques
- Conducting calorimetric experiments
- Data collection and analysis
- Error analysis and improving accuracy
Assessment Methods
- Quizzes and examinations to assess comprehension of theoretical concepts.
- Laboratory reports based on calorimetry experiments.
- Final project: A comprehensive calorimetric study of a reaction or material.
- Teacher: Admin User
- Teacher: Admin User

This course is module 1 of Fundamentals of Food chemistry
- Teacher: Admin User
